

This mechanism can enable data subjects to determine whether their personal information is being processed in line with applicable data protection laws and whether their rights are being upheld. Most data protection laws provide for data subjects to request and be given access to the information being held about them by a controller. In addition to giving effect to the right to privacy, data protection laws also typically facilitate a right of access to information.

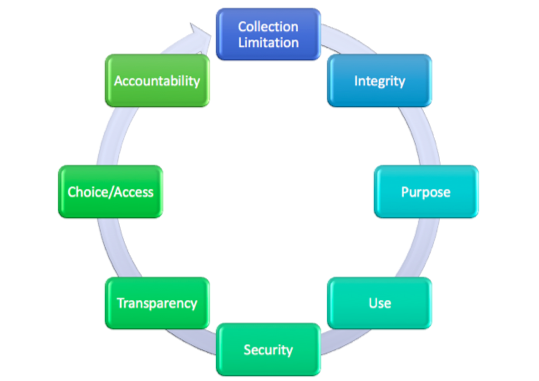
The Personal Data Protection Guidelines for Africa( 1) ( Data Protection Guidelines), a joint initiative of the Internet Society ( ISOC) and the AU, sets out key data protection principles that appear across most frameworks:( 2) While there may be differences across jurisdictions, there are also a number of governing principles that appear in most data protection frameworks.

This module explores data protection authorities in more detail below under Use of data protection authorities to vindicate the right to privacy. A data protection authority is a type of independent authority or public body established to monitor and enforce compliance with a data protection framework.
#Basic data privacy principles manual#
Processing usually refers to a wide range ofactions that can be performed on personal information including collection, organisation, storage, alteration, retrieval, sending, or deletion, and includes both manual and automated means.A data controller, which can typically be either a public or private body, is the person or entity responsible for processing the personal information about the data subject.A data subject is any person to whom this information relates – in other words, a person whose rights are at stake.Personal information or an equivalent term generally refers to any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person which can be used to identify them, whether directly or indirectly, such as their name, contact details, age, race, gender, sexual orientation, health information, financial information, employment details, political or religious views, or biometric information.Data protection laws are aimed at protecting and safeguarding the processing of personal information (or personal data).Īlthough the specific definitions and terms may vary, most data protection laws set out similar basic concepts: Module 4: Privacy and Security Online Key principles for data protectionĭata protection is one of the primary measures through which the right to privacy is given effect.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
